sustainability
Scroll Down
Carbon Savings Impact
Carbon Emission Savings:
Engine idling contributes to carbon emissions because fuel combustion releases carbon dioxide (CO₂). By reducing idle time, significant carbon savings can be achieved.
Per Year (30 seconds):
• Low Estimate: Approximately 419.75 metric tons of CO₂ saved annually.
• High Estimate: Approximately 693.5 metric tons of CO₂ saved annually.
This is half of the savings calculated for 1 minute (which was 839.5– 1,387 metric tons).
2. Equivalent Environmental Benefits
The carbon savings can be equated to environmental activities and impacts for better understanding:
a) Tree Planting Equivalent
•Trees absorb CO₂ as part of their natural process. On average, a tree can absorb 60kg of CO₂ per year.
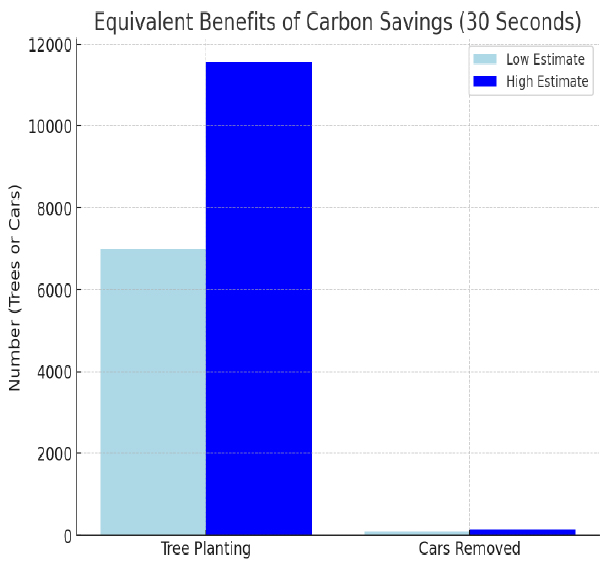
•Savings from 30 seconds of idling:
• Low Estimate: Equivalent to planting 6,996 trees.
• High Estimate: Equivalent to planting 11,558 trees.
b) Cars Removed from the Road
•On average, a car emits 4.6 metric tons of CO₂ annually.
•Savings from 30 seconds of idling:
• Low Estimate: Equivalent to taking 91 cars off the road.
• High Estimate: Equivalent to taking 151 cars off the road
Carbon Savings Impact

3. Visualizing the Impact
If implemented for 100,000 cars daily, saving 30 seconds of idling would:
•Contribute to substantial reductions in urban air pollution, improving public health.
•Demonstrate a scalable model for other cities or sectors.